Plants need nutrients to grow and reach their maximum genetic potential.
There are 17 most important nutrients for plants, all different pieces of the very same puzzle. Plants must obtain these nutrients from their environment and different sources to grow optimally. The three primary nutrients are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K), followed by three secondary nutrients calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg) and sulphur (S) and other eleven micronutrients.
Plants need a permanent availability of all the nutrients in proportion to their daily needs.
These nutrients need to be replenished in the soil after the plant harvest and this is done by the use of organic and/or mineral fertilizers. The objective of balanced fertilization is to ensure that the plant has access to an adequate supply of each nutrient at every growth stage in order to avoid any over or under-supply. This enables the crop to optimise its use of the nutrients and ensures strong, healthy and productive crop growth while minimising environmental impacts.
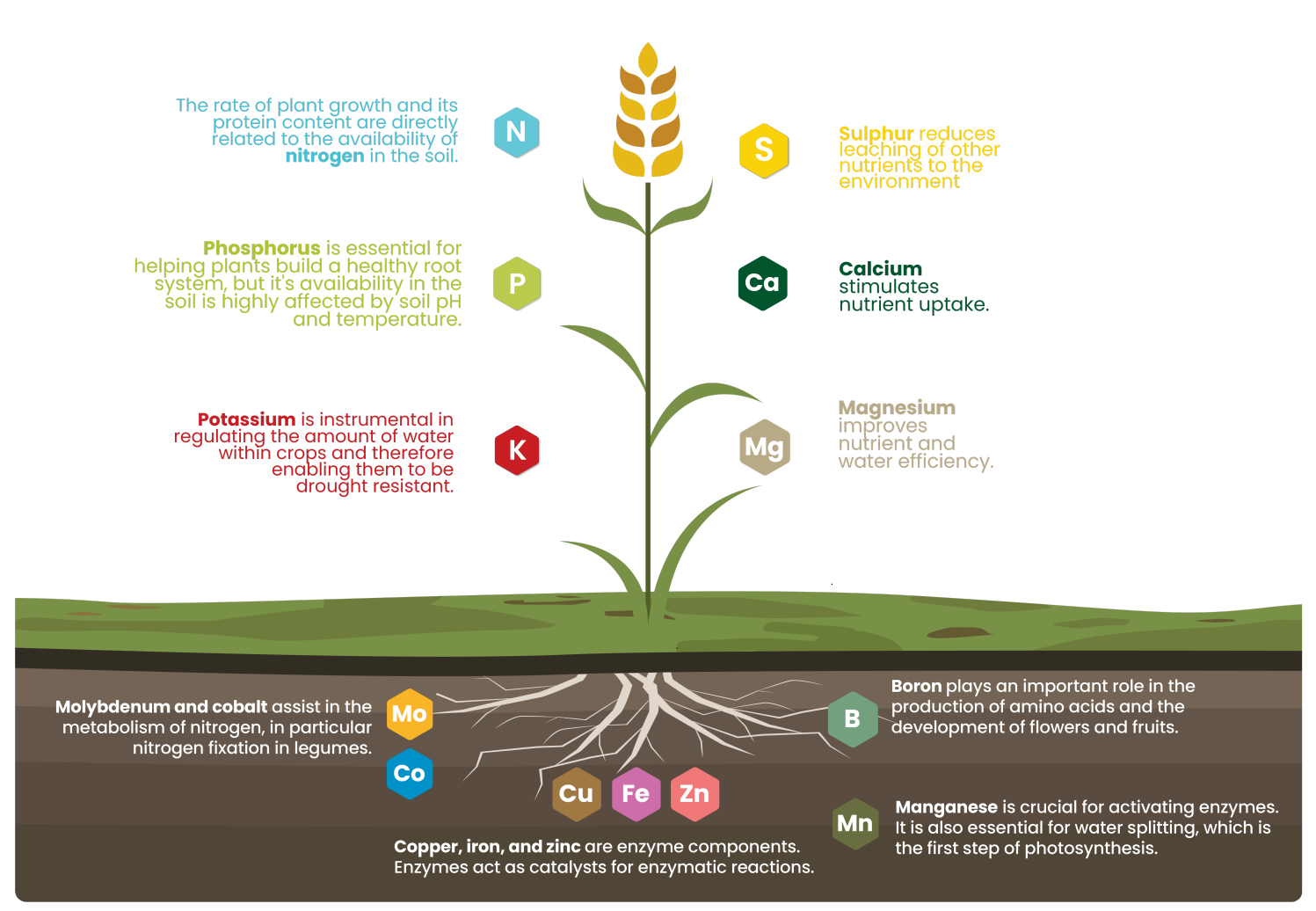
Plants need fertilizers to ensure they receive essential nutrients for healthy growth, development, and reproduction. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Why Do Plants Need Fertilizers?

What Kind of Fertilizers Do Plants Mainly Need?
Plants primarily need three macronutrients in large quantities, along with several micronutrients in smaller amounts. The main types of fertilizers are based on these nutrients:
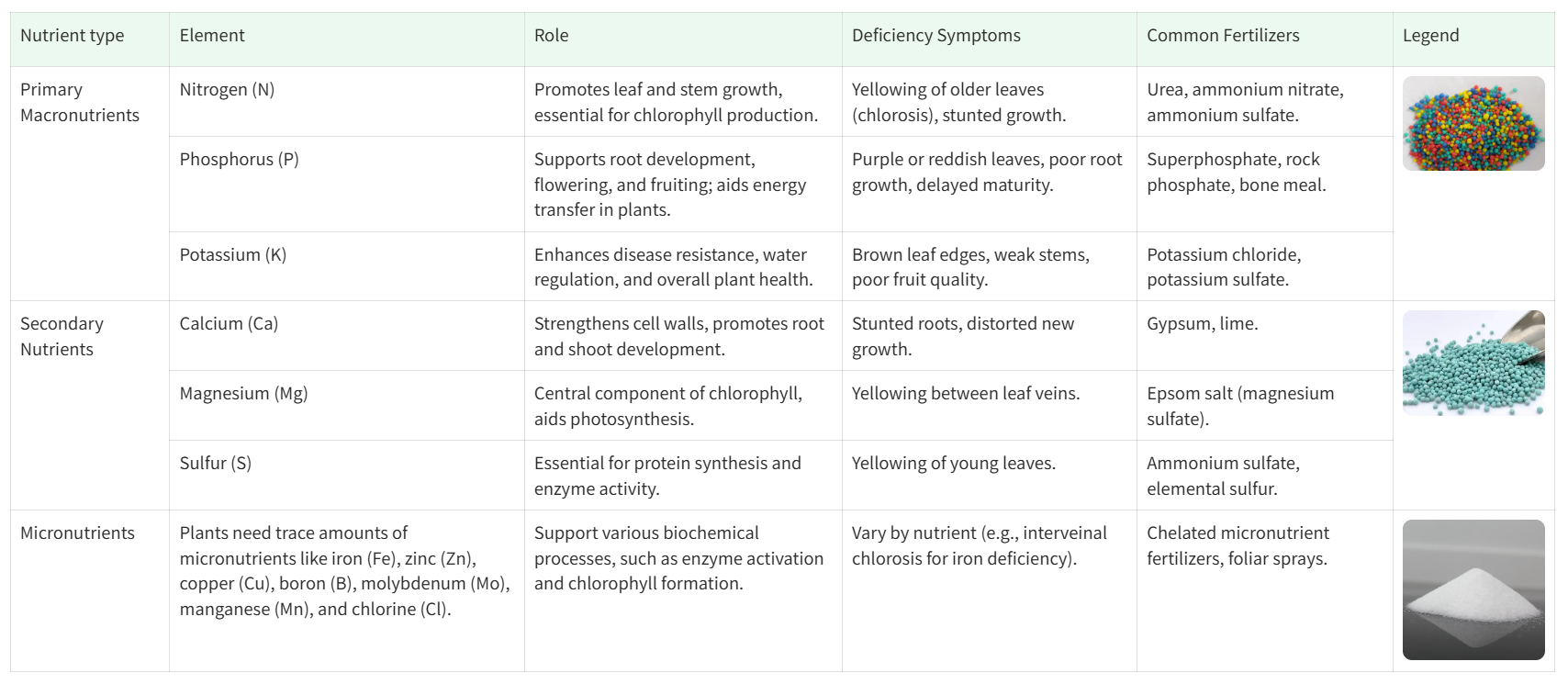
Types of Fertilizers Based on Composition
01 Organic Fertilizers
1.1 Derived from natural sources like compost, manure, bone meal, or fish emulsion.
1.2 Release nutrients slowly and improve soil health.
02 Inorganic (Synthetic) Fertilizers
1.1 Chemically manufactured, providing nutrients in readily available forms.
1.2 Examples: Urea, ammonium nitrate, superphosphate.
03 Complete vs. Incomplete Fertilizers
1.1 Complete fertilizers contain all three primary macronutrients (N-P-K).
1.2 Incomplete fertilizers lack one or more primary nutrients.
04 Slow-Release or Controlled-Release Fertilizers
1.1 Nutrients are released gradually over time, reducing the risk of over-fertilization.
Conclusion
Plants need fertilizers to obtain essential nutrients for growth, development, and reproduction. The main fertilizers they require are those providing nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), along with secondary nutrients and micronutrients. The choice of fertilizer depends on the plant’s specific needs, soil conditions, and growth stage. Proper fertilization ensures healthy plants, higher yields, and improved soil fertility.



