What is Magnesium?
Soil nutrients come in three basic categories: macro, meso and microelements depending on the quantity in which the plants need them. Magnesium (Mg) is an essential meso nutrient, along with calcium (Ca) and sulfur (S).
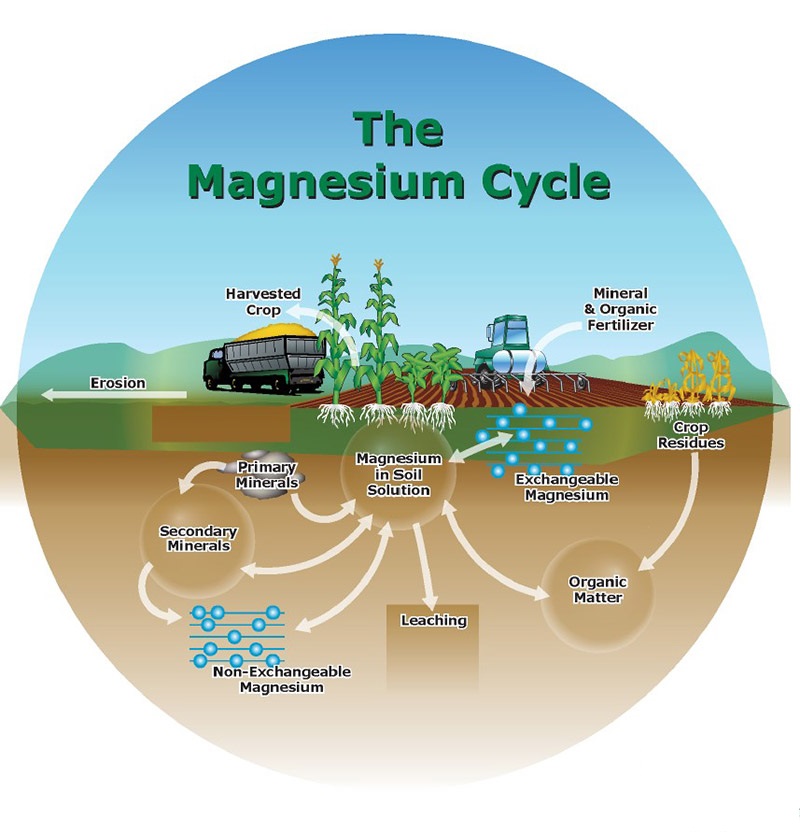
Magnesium is a very mobile element that is important for plant growth and development. Its availability in soil depends on multiple factors: the source rock material, the degree of weathering, local climate and the specific agricultural system and its management practices.
How do plants use Magnesium?
Magnesium is an essential element throughout the whole growth period of a plant. Magnesium fulfills several functions within the plant. It is a central component of chlorophyll which is supporting the function to absorb sunlight during photosynthesis. Magnesium acts as a phosphorus carrier in plants and is essential for phosphate metabolism.
Furthermore, it is also needed for cell division and protein formation, activation of several enzyme systems and is an essential component for plant respiration. In short, without magnesium, chlorophyll cannot capture solar energy for photosynthesis and the important metabolic functions related to carbohydrates and cell membrane stabilization cannot be performed by the plant.

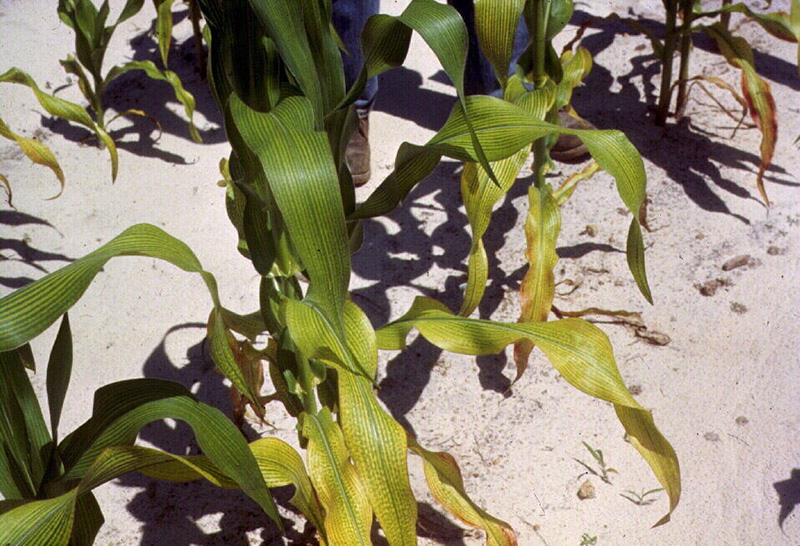
What are the signs of magnesium deficiencies?
Magnesium deficiency commonly occurs in intensively used agricultural soils, but it can also be caused by weathering of soil. It is often seen in sandy, strongly leached and acid soils.
It is not easy to recognize Mg deficiency based on the symptoms. Due to its mobility within the plant, Mg deficiency symptoms will appear on the lower and older leaves first, before the symptoms become visible on the younger leaves.
Common deficiency symptoms include:
- slow growth and leaves to turn yellow, especially on the outer edges, which then developinterveinal chlorosis
- newly growing leaves may become yellow with dark spots
- purple or reddish spots on the leaves

Common magnesium fertilizers
Magnesium fertilizers are divided into water-soluble magnesium fertilizers and slightly soluble magnesium fertilizers. The former include magnesium sulfate, magnesium chloride, and potassium magnesium fertilizers; the latter mainly include ammonium magnesium phosphate, calcium magnesium phosphate, dolomite and magnesite.