What are plant biostimulants?
Plant biostimulant is a product which stimulates plant nutrition processes independently of the product’s nutrient content, with the sole aim of improving one or more of the following characteristics of the plant or the plant rhizosphere: nutrient use efficiency, tolerance to abiotic stress, quality traits, or the availability of confined nutrients in soil or rhizosphere.
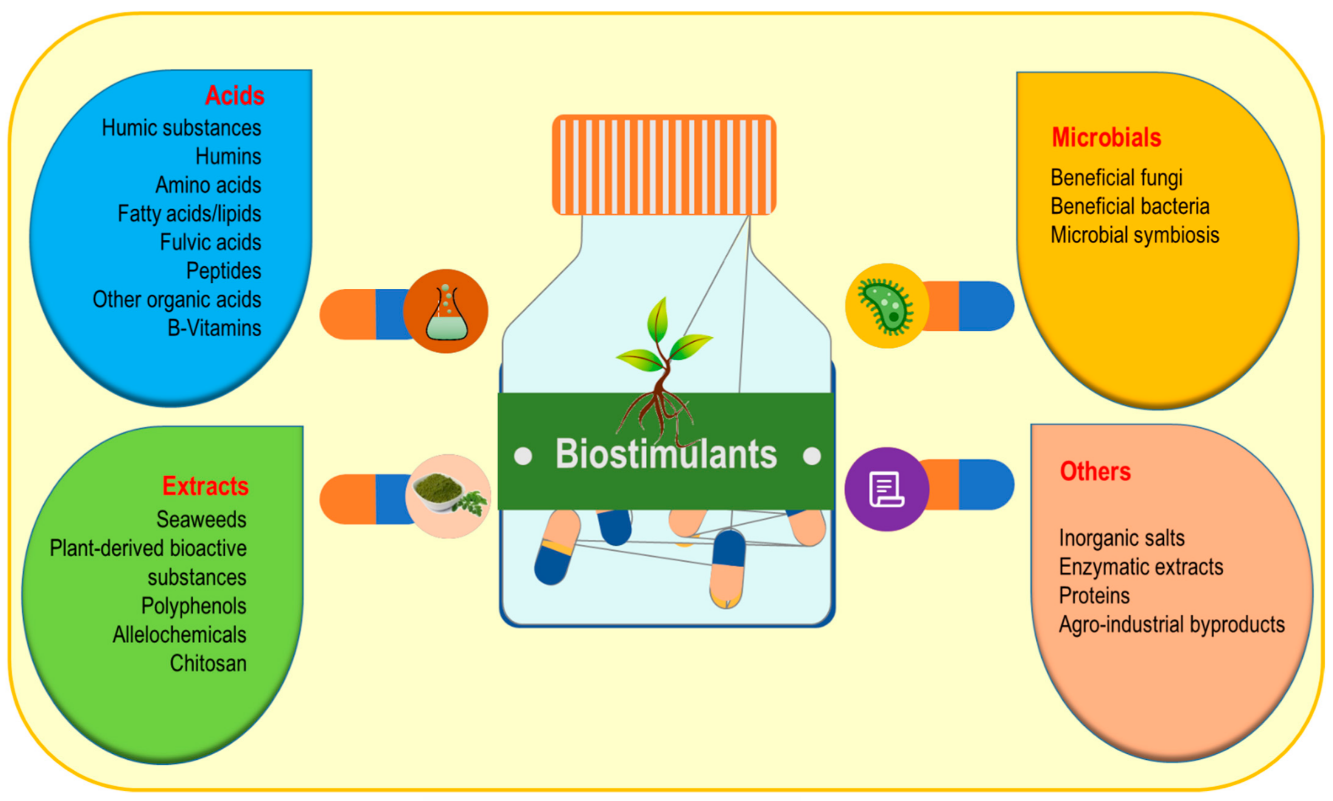
There are many categories of biostimulants. The most popular are humic acids, seaweed extracts, liquid manure composting and beneficial bacteria and fungi.
Humic and fulvic acids – parts of soil organic matter resulting from the decomposition of plant, animal, and microbial residues.
e.g. peat, mineral deposits of leonardite and soft coal
Dark in color
Can increase the cation exchange capacity
Seaweed Extracts
Derived through different extraction processes.
Soluble powders or liquid.
Liquid manure composting
Made by mixing manure water and a blend of proprietary materials thought to feed specific bacteria in the manure. This provides adequate conditions for microbial growth. The liquid is then used as a biofertilizer.
Beneficial bacteria and fungi – concentration of bacteria and/or fungi in the soil that help with root growth.
E.g. Bacillus and Rhizobium fungi
Majority of products marketed toward large scale commercial agriculture
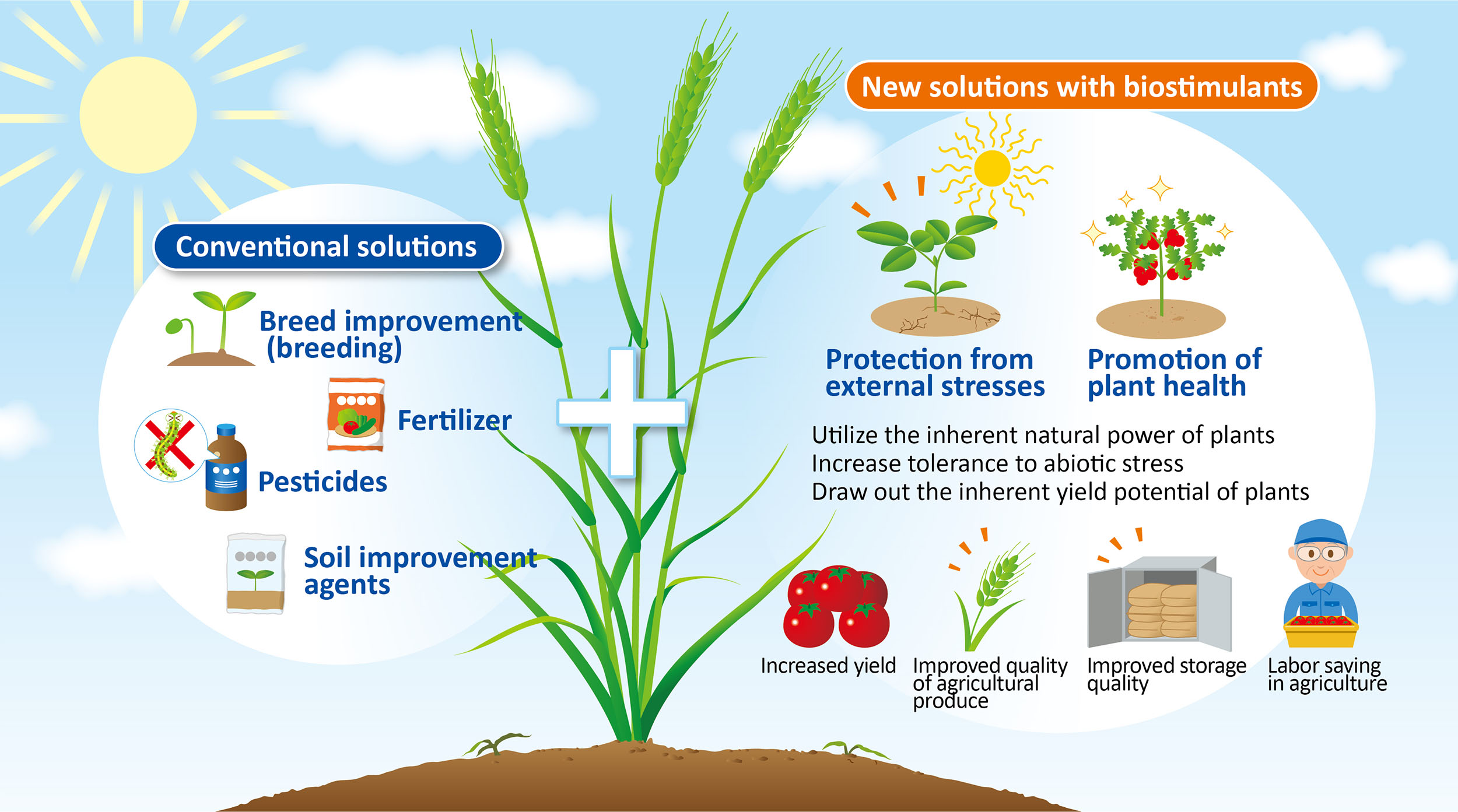
Why are plant biostimulants useful?
Biostimulants are increasingly recognised for their role in sustainable food systems. They support farmers and the food supply chain by enhancing crop yield and quality, improving nutrient use efficiency, and helping plants withstand environmental stress.
Global food security is a pressing issue influenced by climate change, geopolitical factors, and the availability and affordability of crop inputs for farmers. Plant biostimulants can significantly support food security by increasing crop yield, improving nutrient use efficiency and relieving plants from climate-related stress.
Plant biostimulants are useful in many key areas:
Productivity: plant biostimulants offer innovative, science-based solutions improve yield and quality
Agronomic: plant biostimulants improve the efficacy and efficiency of other inputs
Environmental: plant biostimulants help mitigate environmental concerns
Economic: plant biostimulants strengthen farmer profitability
Sustainability: plant biostimulants help meet the demand for more sustainable food production.
The benefits of plant biostimulants
Biostimulants can increase nutrient use efficiency so that farmers receive a better return on their fertiliser investment. This includes making use of nutrients in the soil that might not otherwise be available to plants, for example by solubilising phosphorus into plant-available forms. These nutrient-use improvements reduce nutrient losses and their related environmental impacts. The link between good nutrition and high yields is well established.
Biostimulants also help plants to better tolerate abiotic stresses such as drought, extreme temperatures, salinity, and flooding. Although it is not their primary reason for use, making plants more vigorous in the face of abiotic stresses is likely to make them less vulnerable to disease in the same way that you are less likely to fall ill if you eat a healthy, balanced diet.
Many plant biostimulants encourage better root systems, which speeds up crop establishment.
All of these benefits have been widely tested and documented in field trials. The overall benefit is an increase in marketable yield and quality. Yield increases related to biostimulant use are reported to be at least 5 – 10%.




